Overview
Working in Thailand comes with tax obligations that both employers & employees must be aware of. From personal income tax to social security contributions, understanding the taxation system helps both parties to remain fully compliance and legally protected.
Key Regulations
Personal Income Tax
Under current regulations (effective from 1 January 2024), Thai residents are subjected to personal income tax on worldwide income on the portion of income that is brought into Thailand, regardless of where the income was paid or when the income was originally earned. Non-Thai residents on the other hand are taxed from employment or business carried on in Thailand, regardless of where it’s paid from.
Withholding Taxes
Employers must withhold personal income tax from employees’ salaries each month based on progressive tax rates. The withheld tax has to be reported and remitted to the Revenue Department with Form PND 1. At the end of the year, employers have to issue Withholding Tax Certificate (Form 50 Tawi) for staff to file their annual return.
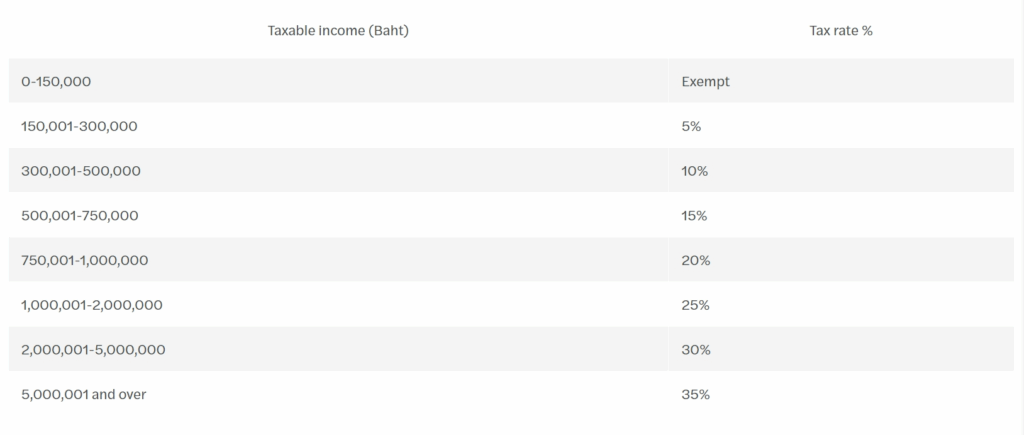
Progressive Tax Rate 2025
Annual Tax Filing
Employees must file an annual tax return (Form PND 90/9) by March 31 of the following year. If taxes withheld during the year are more than final tax due, employees can claim a refund. If however the taxes withheld are not enough, the balance must be paid with the filing.
Summary
• Employee income in Thailand is taxed progressively, with rates ranging from 0% to 35%.
• Employers are responsible for withholding tax each month.
• Employees can benefit from deductions and allowances to reduce their tax liability.
• Annual tax filing is mandatory for all employees, even if tax is fully withheld at source.
เรียบเรียงโดย : www.aplthailand.com
Credit Picture : www.pixabay.com

